What diuretics are used in the treatment of edema syndrome
Since ancient times, diuretics have been used for edema to expel excess fluid from the body. For the first time, a mercury diuretic (calomel) was used by Paracelsus to treat edema. Modern medicine has a large arsenal of diuretics of various actions. But they must be used strictly according to the doctor's prescription in order to avoid severe violations of electrolyte homeostasis and kidney damage.

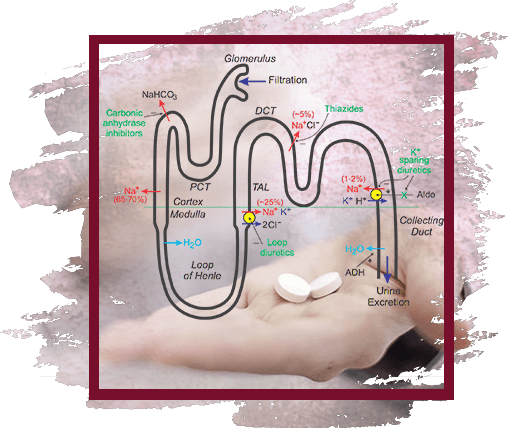
Diuretics are classified based on the point of application of their action in the nephron, the main structural and functional unit of the kidney. The nephron consists of the renal corpuscle, where the blood is filtered and the primary urine is formed, and the tubular system, where reabsorption (i.e. reabsorption) occurs. The urine then exits through the collecting ducts.
Among the diuretics acting in the proximal (near) tubule, there are 2 groups - carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and osmotic diuretics.
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors block this enzyme, and therefore a large number of negatively charged bicarbonate ions accumulate in the lumen of the tubules, as a result, the amount of urine and its acidity increase.
The main representative of carbonic anhydrase blockers is diacarb. Its diuretic activity is low, therefore, it is not used to treat severe edema syndrome. It must be used in courses - after 3-4 days of admission, take a break to avoid metabolic acidosis.
Osmotic diuretics keep sodium and water in the tubule lumen. Most often, mannitol is used, which is characterized by a pronounced and rapidly onset diuretic effect, which is necessary for patients in critical conditions. It is used mainly in intensive care units, since it is effective only when administered intravenously and is characterized by a large number of dangerous side effects.
The main drugs for the treatment of edema syndrome are loop and thiazide diuretics.
Loop diuretics
They act in the thick (ascending) segment of the Henle loop. Most drugs in this group are strong diuretics that are active both when taken orally and when administered intravenously. They are successfully used for the treatment of edema syndrome in kidney disease and chronic heart failure.
Loop diuretics are the only group of diuretics used for chronic renal failure.
One of the most widely used loop diuretics is furosemide, but the most effective of all is torasemide, which is 2 times more bioavailable. If the effectiveness of furosemide is significantly reduced with a lack of albumin, then torasemide has practically no affinity for albumin.
Torasemide is a loop diuretic that simultaneously has the properties of an aldosterone antagonist and therefore slows down the rate of progression of chronic heart failure and reduces mortality from it.
When using inadequate doses of loop diuretics, violations of electrolyte homeostasis (a decrease in potassium, sodium, magnesium, calcium) can be observed, therefore it is necessary to control the content of electrolytes in blood biochemistry. Also, when prescribing furosemide, it is necessary to donate blood for albumin content.
Loop diuretics should be used with caution with certain antibiotics (gentamicin, kanamycin, streptomycin) due to the risk of deafness.
Thiazide diuretics
It is the first class of diuretics specifically synthesized to target specific segments of the nephron. They were originally obtained by accident in the late 1940s in the process of searching for a drug that would slow down the elimination of penicillin, which was not readily available in those years.
They are also used to treat hypertension. They are used only in the form of tablets, there are no solutions for parenteral administration; they act in the region of the distal tubules.
The diuretic activity of thiazide diuretics is weaker than loop diuretics, but they are successfully used to treat edema of any origin, as well as in diabetes insipidus and hypercalcemia.
One of the most commonly used diuretics in this group is hypothiazide. There are thiazide-like diuretics, such as indapamide, but they do not have a clear diuretic effect.
Potassium-sparing diuretics
They act in the area of the collecting ducts and therefore have a very weak diuretic effect, but they are successfully used in combination with loop and thiazide diuretics.
In order to stimulate diuresis, aldosterone antagonists are rarely used today, mainly when edema develops due to an excess of aldosterone, for example, in decompensated liver cirrhosis.

Basic rules for the treatment of edema syndrome
- Strictly observe the prescribed dosage of diuretics and other doctor's recommendations.
- Do not use drugs that aggravate edema (calcium antagonists, nonspecific anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticosteroids).
- Refuse to accept table salt as much as possible.
- Stay more in a sitting position, and not lying or standing.
- Control the water balance (the amount of liquids drunk and secreted, weight).
- Monitor your condition (blood pressure and heart rate).
- Donate blood periodically to monitor electrolyte balance.
 DE
DE FR
FR IT
IT ES
ES